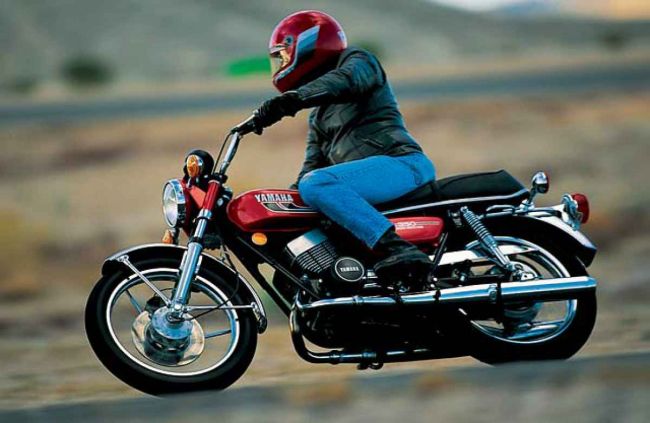
I always wonder why Yamaha RX 100 and Yamaha RD 350 are being vowed by the entire biker community of India, even today after decades of these bikes being discontinued from the market they are still in demand among the bikers in the after market. Both the bikes and bikes like Suzuki Shogun and Suzuki Shaolin are few other bikes to name which belong to the Elite group of bikes having 2-Stroke Engines. However the modern Motorcycle era belongs to the 4-Stroke engines but these 2-stroke engine bikes have become immortal and if I call them Legends that must not be the exaggeration at all.

The 2-Stroke Engines are actually simple internal combustion engines they are even simpler then 4-Stroke Engines. As we also faced complications while understanding the mechanism of 2-stroke engines explained in other sites available on Net, we would try to explain you the working of 2-stroke engines in simple and easy terms. To begin with one should understand that, one thing is common between both 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines and that is both are "engines" and the job of an engine is to produce power and torque by using mixture of Air and Fuel.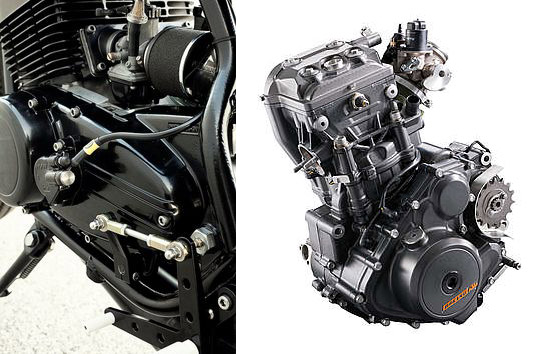
The Engine mainly consists of Head and Block, the Head contains the Spark plug and in case of 4-stroke engines it also consists of inlet and outlet Valves. The Block contains Piston, Crankshaft and Connecting rod. The space between the Head and Block where there is actual combustion of mixture of the fuel and air takes place is called Combustion Chamber.
The process of combustion starts when the mixture of Fuel and Air gets ignited by the spark obtained from the Spark plug causing blast in the combustion chamber of the engine, thereby thrusting the piston downwards moving the Crank shaft which is attached with the piston through connecting rod. Each time the Piston moves forward and backward gets the Crankshaft also turn and thereby turning the wheels through the Transmission. That is how the Fuel turns into forward motion. There are four basic processes involved to complete one cycle of combustion in both 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines, namely: Intake, Compression, Ignition and Exhaust.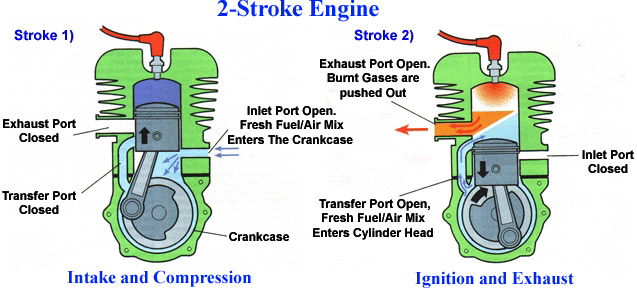
A stroke is called one movement of the piston, either forward or backward and in 2-stroke engines as the term itself suggests the entire combustion process completes in only 2 strokes i.e. Intake of fresh fuel and air mixture and Compression of the mixture of the fuel and air present in the combustion chamber from the last stroke takes place in one stroke and with the blast at the end of the first stroke, Ignition takes place propelling the piston downwards and consequently opening the Exhaust port to let the burnt residual gases out from the exhaust thereby completing the combustion cycle in just 2-strokes of the piston (two processes at each stroke) and hence it is called 2-stroke engine.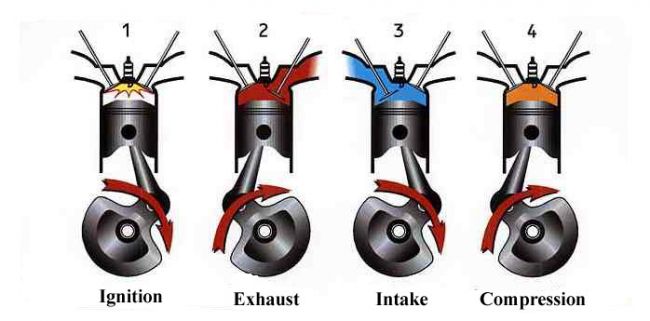
To complete the cycle of combustion in 4-stroke engines it takes four strokes of the piston, it means every single stroke carries out one of the four processes of the Combustion. While the piston goes down for the first time the inlet valve gets open drawing the mixture of fuel and air to the combustion chamber and then in the second stroke while the piston is coming back towards the top it Compresses the gas drawn in the first stroke and at the end of the second stroke the spark plug gets ignited and the Ignition takes place, with the force generated from the blast the piston goes down for the third stroke and finally the piston goes up with the Exhaust Valve open to expel the spent gasses out and there by completing all the four process of Combustion in 4 strokes of the piston hence the engine is called 4-stroke engine.
The 2-stroke engines are being discontinued mainly due to its polluting nature and poor mileage. The strict emission norms didn't tolerate the polluting nature of two stroke engines, as the entire combustion cycle completes in 2 strokes of piston mixing of spent gasses and the mixture of fresh fuel and air becomes inevitable making the two stroke engines not only polluting in nature but poor at fuel economy also.
Whatever the reasons given it may be, every true biker from heart always wants 2-stroke bikes back accepting all its drawbacks. Even today I dream of a brand new Yamaha Rd 350 with all modern gadgetry, new chassis and improved 350cc twin cylinder 2-stroke engine with Fuel Injection system producing 70Bhp of raw pulsating power.
What do you think of it guys? Please do share your thoughts.
By: Farhan Kashif

What is that which makes these bikes special? Is it the Brute performance, which these bikes are capable off delivering? or the mind numbing Pick-up they have to offer? Whatever the answer is, it is the 2-Stroke engine which is actually responsible for all these divine experiences. Now there are many questions arise in mind when we talk about these 2- Stroke engine, which we would discus step by step:
How 2-Stroke Engines Work?
The 2-Stroke Engines are actually simple internal combustion engines they are even simpler then 4-Stroke Engines. As we also faced complications while understanding the mechanism of 2-stroke engines explained in other sites available on Net, we would try to explain you the working of 2-stroke engines in simple and easy terms. To begin with one should understand that, one thing is common between both 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines and that is both are "engines" and the job of an engine is to produce power and torque by using mixture of Air and Fuel.

Engine:
The Engine mainly consists of Head and Block, the Head contains the Spark plug and in case of 4-stroke engines it also consists of inlet and outlet Valves. The Block contains Piston, Crankshaft and Connecting rod. The space between the Head and Block where there is actual combustion of mixture of the fuel and air takes place is called Combustion Chamber.
Combustion:
The process of combustion starts when the mixture of Fuel and Air gets ignited by the spark obtained from the Spark plug causing blast in the combustion chamber of the engine, thereby thrusting the piston downwards moving the Crank shaft which is attached with the piston through connecting rod. Each time the Piston moves forward and backward gets the Crankshaft also turn and thereby turning the wheels through the Transmission. That is how the Fuel turns into forward motion. There are four basic processes involved to complete one cycle of combustion in both 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines, namely: Intake, Compression, Ignition and Exhaust.

2-Stroke Engines:
A stroke is called one movement of the piston, either forward or backward and in 2-stroke engines as the term itself suggests the entire combustion process completes in only 2 strokes i.e. Intake of fresh fuel and air mixture and Compression of the mixture of the fuel and air present in the combustion chamber from the last stroke takes place in one stroke and with the blast at the end of the first stroke, Ignition takes place propelling the piston downwards and consequently opening the Exhaust port to let the burnt residual gases out from the exhaust thereby completing the combustion cycle in just 2-strokes of the piston (two processes at each stroke) and hence it is called 2-stroke engine.

4-Stroke Engines:
To complete the cycle of combustion in 4-stroke engines it takes four strokes of the piston, it means every single stroke carries out one of the four processes of the Combustion. While the piston goes down for the first time the inlet valve gets open drawing the mixture of fuel and air to the combustion chamber and then in the second stroke while the piston is coming back towards the top it Compresses the gas drawn in the first stroke and at the end of the second stroke the spark plug gets ignited and the Ignition takes place, with the force generated from the blast the piston goes down for the third stroke and finally the piston goes up with the Exhaust Valve open to expel the spent gasses out and there by completing all the four process of Combustion in 4 strokes of the piston hence the engine is called 4-stroke engine.
Difference Between 2-Stroke Engines And 4-Stroke Engines:
- Two Stroke Engines can be identified by its distinctly loud and sharp sound, whereas 4-stroke engines have subdued sound with distinct- Purr.
- The 2-Stroke engines are simple and light weight, where as 4-stroke engines are heavy and complexed in nature.
- The 2-stroke engines are quicker in acceleration then the 4-stroke engines as they complete the combustion cycle in almost half the time that any 4-stroke engine takes to complete.
- Two stroke engines produce almost double the power then its same sized 4-stroke engine counterparts.
- Two Stroke engines are cheaper to produce as there are less components used then 4-stroke engines.
- The 2-Stroke engines are considered more vulnerable as there is no dedicated lubrication system in it hence if ignored damage to the engine is inevitable.
- The 2-stroke engines are fast and quick in acceleration but are suicidal in long journeys with its poor lubrication system and fast engine wear and tear where as 4-stroke engines are considered as long lived engines even when used in long journeys riding continuously at very high speeds.
- Two stroke engines are easy to maintain as compare to the 4-stroke engines

Why 2-Stroke Engines Are Discontinued?
The 2-stroke engines are being discontinued mainly due to its polluting nature and poor mileage. The strict emission norms didn't tolerate the polluting nature of two stroke engines, as the entire combustion cycle completes in 2 strokes of piston mixing of spent gasses and the mixture of fresh fuel and air becomes inevitable making the two stroke engines not only polluting in nature but poor at fuel economy also.
Whatever the reasons given it may be, every true biker from heart always wants 2-stroke bikes back accepting all its drawbacks. Even today I dream of a brand new Yamaha Rd 350 with all modern gadgetry, new chassis and improved 350cc twin cylinder 2-stroke engine with Fuel Injection system producing 70Bhp of raw pulsating power.
What do you think of it guys? Please do share your thoughts.
By: Farhan Kashif











