 According to the old saying “The More The Merrier” (Which is also a movie), more of a good thing is always better. Sure this saying holds true for family picnics and house parties but believe It or not that those small explosions happening in multiple of thousands inside your bike's engine can damage internal assembly if taken beyond a recommended limit, crazy right? Who knew? But fear not in today’s age there is a possible solution for almost every mechanical problem. The solutions name, in this case, is a “Rev-limiter”. The name is pretty self-explanatory because it limits the number of Revs inside the internal combustion engine if we intend to take it beyond its intended physical capabilities.
According to the old saying “The More The Merrier” (Which is also a movie), more of a good thing is always better. Sure this saying holds true for family picnics and house parties but believe It or not that those small explosions happening in multiple of thousands inside your bike's engine can damage internal assembly if taken beyond a recommended limit, crazy right? Who knew? But fear not in today’s age there is a possible solution for almost every mechanical problem. The solutions name, in this case, is a “Rev-limiter”. The name is pretty self-explanatory because it limits the number of Revs inside the internal combustion engine if we intend to take it beyond its intended physical capabilities.Working on internal combustion engine and function of Rev Limiter:
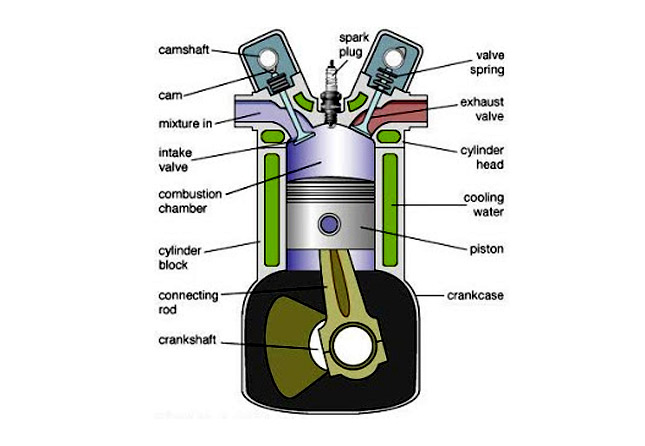 Every IC engine includes following:
Every IC engine includes following:• Inlet and outlet Valves
• Camshaft
• Cylinder block
• Connecting Rod
• Crankshaft
• Crankcase
• Piston
• Cylinder Head
• Valve spring and Sparkplug
• Camshaft
• Cylinder block
• Connecting Rod
• Crankshaft
• Crankcase
• Piston
• Cylinder Head
• Valve spring and Sparkplug
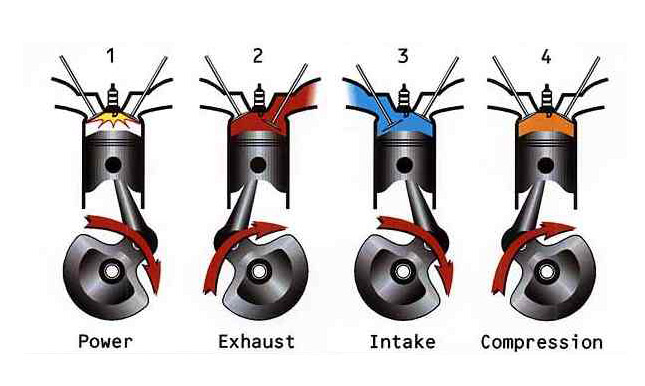
Working of this elaborate mechanical device is pretty simple, there are 2 terms related to the IC engine i.e. Bore and Stroke. Bore represents the diameter of the piston and a stroke represents the full travel of the piston along the cylinder in any direction. When an engine says 4 strokes then it means that the engine completes 4 separate strokes to complete a single thermodynamic cycle during two separate revolutions of the crankshaft. The four strokes are named as intake, compression, power and exhaust.
The piston rods are attached to the crankshaft, which connects the pistons. When the crankshaft turns it causes the pistons to move up and down. Above the crankshaft the camshaft is connected, which is connected to the crankshaft by a timing belt. The camshaft opens and closes the valves.
First intake stroke causes the inlet valve to open and allow the fuel-air mixture to come in and the piston travels down simultaneously. Second compression stroke makes the inlet valve to close and the piston travels up compressing the fuel-air mixture before the piston can hit the top of the compression stroke a spark ignites the fuel-air mixture, this causes the explosion and the third stroke is known as combustion stroke. The piston travels down due to the pressure generated by the explosion and the engine receives its power. This brings forth the fourth stroke, the exhaust valve is opened and the exhaust gases are sent outside the same valve. This process is repeated in multiples of thousands per minute to make your motorcycle go fast.
 What this process of revving the engine is increased to a higher point that the engine is capable of then the process is known as “over-revving”. Rev limiter works by limiting the revs by using different methods even if the throttle is wide open. Almost all the performance bikes are equipped with this device and recently entry-level motorcycles like KTM RC 390 also come equipped with the same. The basic working of a rev limiter involves cutting off one of the many components needed for the combustion process. A rev limiter either controls ignition timing, spark or fuel to the injectors.
What this process of revving the engine is increased to a higher point that the engine is capable of then the process is known as “over-revving”. Rev limiter works by limiting the revs by using different methods even if the throttle is wide open. Almost all the performance bikes are equipped with this device and recently entry-level motorcycles like KTM RC 390 also come equipped with the same. The basic working of a rev limiter involves cutting off one of the many components needed for the combustion process. A rev limiter either controls ignition timing, spark or fuel to the injectors.Working of the Rev-limiter:
A rev limiter can use following types of methods to control high revs-
Spark control:
When the motorcycle reaches redline the engine closes the spark. This method is not very sustainable as the system keeps injecting the fuel into the cylinder and keeps releasing it without combustion, from the exhaust pipe. This type of control affects much internals of the bike including by the catalytic converter. When the RPM is dropped below the limit, the spark is restored. Usually, in this case, the primary peak voltage required to cause the spark is reduced as a result the ignition does not take place.
Fuel control:
Fuel control regulates the fuel flow into the cylinder and only the air goes in and comes out. Once the engine is at redline, the fuel supply into the cylinder is restricted and a lot of air enters, this causes the air-fuel mixture to become lean which refers to the burning of fuel with an excess of air in the IC engine. Engines used in this process can support higher compression ratios and provide better performance; this also increases the fuel usage and makes the engine more efficient.
In both of these cases, there is a hard-cut and a soft-cut type of rev limiting. Hard cut simply cuts either the spark or fuel completely. This type of system causes the RPM needle to linger between the set RPM point and a little below it because, at the set RPM limit, the fuel or the spark is cut which causes the RPM to lower down, which restores the spark or fuel causing the RPM TO again increase. Soft limiters partially cut the spark or fuel supply before reaching the set RPM, allowing it to climb slowly and then remain at the set limit.When the motorcycle reaches redline the engine closes the spark. This method is not very sustainable as the system keeps injecting the fuel into the cylinder and keeps releasing it without combustion, from the exhaust pipe. This type of control affects much internals of the bike including by the catalytic converter. When the RPM is dropped below the limit, the spark is restored. Usually, in this case, the primary peak voltage required to cause the spark is reduced as a result the ignition does not take place.
Fuel control:
Fuel control regulates the fuel flow into the cylinder and only the air goes in and comes out. Once the engine is at redline, the fuel supply into the cylinder is restricted and a lot of air enters, this causes the air-fuel mixture to become lean which refers to the burning of fuel with an excess of air in the IC engine. Engines used in this process can support higher compression ratios and provide better performance; this also increases the fuel usage and makes the engine more efficient.
Final thoughts:
Over-Revving our engine is something that almost all of us do unknowingly every day and the harmful effects of this mistake range from damage to internal components, overheating, and valve float, which refers to the inability of the valve springs to keep up with the crankshaft at high RPM’s due to springs own inertia, as a result in MotoGP titanium valve springs are used because less weight equals less inertia. So there you have it, the importance of Rev Limiters and how it works every time we ride to make our engine last long.
For everything related to bikes stay tuned to BikesMedia.
By: Yetnesh Dubey











