The generation born in the 90’s knows Bajaj Pulsar as a household name. It is a motorcycle, whose story we don’t have to listen from our elders because we have grown up with it, literally. When we were teenagers we were presented with a simple design Pulsar, capable of everyday motorcycling needs and a little fun on empty roads. Now, when all of us have grown up, we have Pulsars which can scream their way up to 150 km/h. that’s the kind of relationship our generation has with the Pulsar. So let's take some time out in reliving its history.
The generation born in the 90’s knows Bajaj Pulsar as a household name. It is a motorcycle, whose story we don’t have to listen from our elders because we have grown up with it, literally. When we were teenagers we were presented with a simple design Pulsar, capable of everyday motorcycling needs and a little fun on empty roads. Now, when all of us have grown up, we have Pulsars which can scream their way up to 150 km/h. that’s the kind of relationship our generation has with the Pulsar. So let's take some time out in reliving its history.2001:
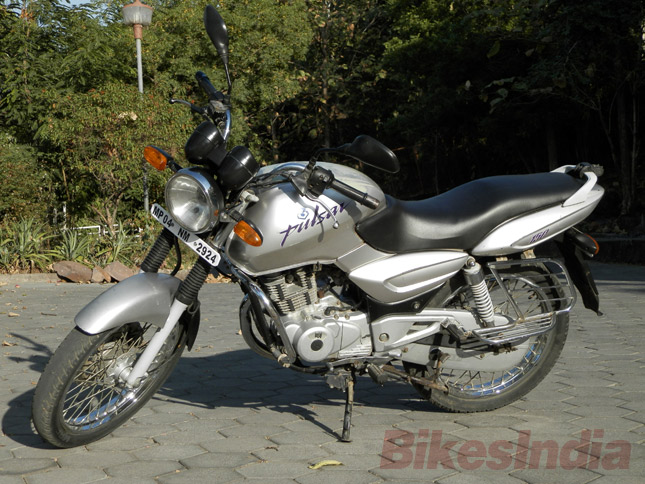 The famous Duo, Pulsar 150 and 180 was born in November 2001. It was an attempt by Bajaj to become one of the key players in the changing Indian Motorcycling market. In 1999, Hero Honda had released their CBZ, which would start the whole craze of performance motorcycles in India, but that’s a story for another time.
The famous Duo, Pulsar 150 and 180 was born in November 2001. It was an attempt by Bajaj to become one of the key players in the changing Indian Motorcycling market. In 1999, Hero Honda had released their CBZ, which would start the whole craze of performance motorcycles in India, but that’s a story for another time.Coming back to the first generations Pulsars, they had a simple design. The round headlight looked retro and the sculpted fuel tank looked modern. Just like the year 2001, the pulsar launched during this time had a reminiscence of past as well as the present. Both motorcycles had a 4-stroke 2 valve air cooled engine, which worked quite well. Pulsar 180 became the performance standard among enthusiast, but it was the P150, which brought in major sales.
2003:
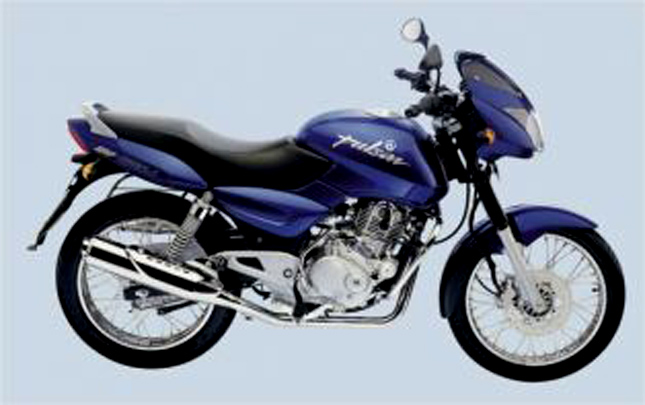 After receiving several bikes of the year awards, Bajaj decided to upgrade both the horses in its stable. During this year, the iconic twin headlamps were included in the motorcycle and the patented DTs-I also made its way into both the bikes and these bikes known as "UG-I". DTs-I meant that these motorcycles would now become better performers while returning top of the line fuel economy. Over the years Bajaj has perfected this technology, which is one of the reasons why the modern Pulsar 150 returns a mileage of over 50 km/l.
After receiving several bikes of the year awards, Bajaj decided to upgrade both the horses in its stable. During this year, the iconic twin headlamps were included in the motorcycle and the patented DTs-I also made its way into both the bikes and these bikes known as "UG-I". DTs-I meant that these motorcycles would now become better performers while returning top of the line fuel economy. Over the years Bajaj has perfected this technology, which is one of the reasons why the modern Pulsar 150 returns a mileage of over 50 km/l.2005-2006:
 It was the year when the identical twins, the Pulsar 180 and Pulsar 150 were made visually different. The 180 was given blacked out alloy wheels and engine, while the 150 was still having Grey coloured alloy wheels. Nitrox suspensions were included in the front and back along with the exhaust- tech.
It was the year when the identical twins, the Pulsar 180 and Pulsar 150 were made visually different. The 180 was given blacked out alloy wheels and engine, while the 150 was still having Grey coloured alloy wheels. Nitrox suspensions were included in the front and back along with the exhaust- tech. In 2006, there wasn’t any mechanical improvement instead the motorcycles were given the famous twin led-strip tail lights. The design of the rear body panel was also changed to a sharper and sleeker look.
2007:
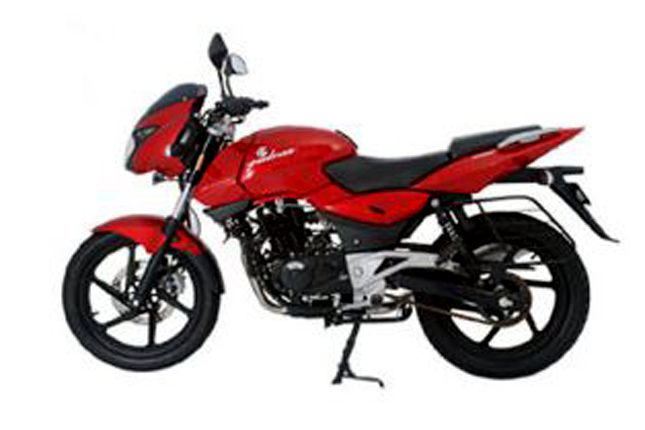 Two of the fastest Pulsar bikes were launched in this year. They were the Pulsar 200 and the Pulsar 220-Fi. Pulsar 200 was in an avatar which looked similar to modern-day pulsar 150 and 180. It had a redesigned tank, side panels, tank shrouds, head-light and grab rails. The Pulsar logo was made 3-D and the switches on the bike were made back-lit. The motorcycle had a 200cc Oil cooled 4-stroke 2 valve engine which produced around 18 BHP of power and 17 NM of torque. The motorcycle would later lend it’s design to Pulsar 180 and 220-S (Street).
Two of the fastest Pulsar bikes were launched in this year. They were the Pulsar 200 and the Pulsar 220-Fi. Pulsar 200 was in an avatar which looked similar to modern-day pulsar 150 and 180. It had a redesigned tank, side panels, tank shrouds, head-light and grab rails. The Pulsar logo was made 3-D and the switches on the bike were made back-lit. The motorcycle had a 200cc Oil cooled 4-stroke 2 valve engine which produced around 18 BHP of power and 17 NM of torque. The motorcycle would later lend it’s design to Pulsar 180 and 220-S (Street).
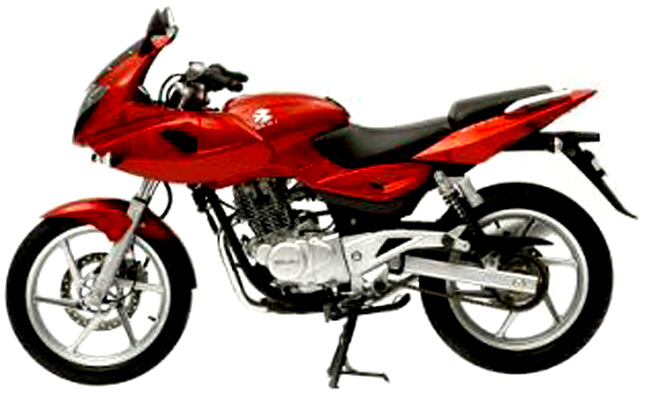 Pulsar 220Fi was a revolutionary motorcycle, it featured Clip-on handlebars, projector headlamps mounted on a half-fairing, split seats, rear disc brakes and most importantly a 220 cc oil-cooled engine which produced 19 BHP of power. It was a powerhouse which had a top speed of 138 km/h, and even more, if someone was crazy enough. The Fi version wasn’t successful in making a dent in the market, so the company relaunched the motorcycle with the carb variant and it started selling all over the country.
Pulsar 220Fi was a revolutionary motorcycle, it featured Clip-on handlebars, projector headlamps mounted on a half-fairing, split seats, rear disc brakes and most importantly a 220 cc oil-cooled engine which produced 19 BHP of power. It was a powerhouse which had a top speed of 138 km/h, and even more, if someone was crazy enough. The Fi version wasn’t successful in making a dent in the market, so the company relaunched the motorcycle with the carb variant and it started selling all over the country. 2009-2010:
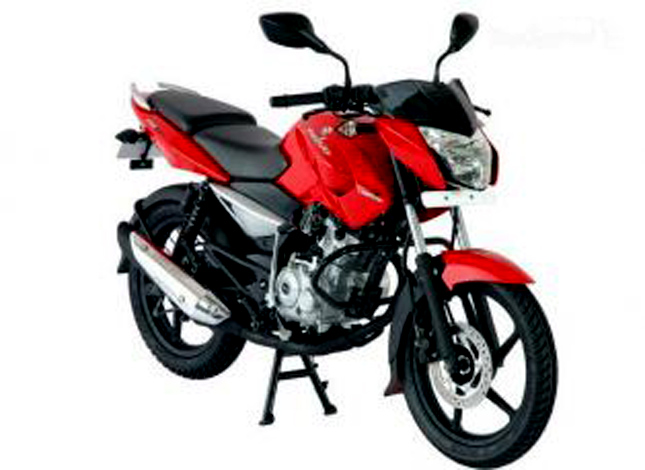 In 2009, Bajaj launched the Pulsar 135 LS, where LS stood for 'Light Sports'. The bike was mainly meant to be used for two reasons, a more approachable Pulsar for everyday riding and a light-weight stunt bike. It had a unique design, quite different from the rest of the Pulsar family, but features like the twin Led strips, back-lit switches and the Pulsar name-tag made it a member. It was the first bike from the house of Bajaj featured with 4-Valve setup.
In 2009, Bajaj launched the Pulsar 135 LS, where LS stood for 'Light Sports'. The bike was mainly meant to be used for two reasons, a more approachable Pulsar for everyday riding and a light-weight stunt bike. It had a unique design, quite different from the rest of the Pulsar family, but features like the twin Led strips, back-lit switches and the Pulsar name-tag made it a member. It was the first bike from the house of Bajaj featured with 4-Valve setup.2010 saw the rebranding and retuning of the flagship models. Pulsar 220Fi was rebranded as Pulsar 220F DTS-I as the fuel injection was replaced with a carb unit. The same 220 cc engine was also made available in a 200cc styled Pulsar, which was named as Pulsar 220 Street. This motorcycle had the looks of a 180 and 200 cc pulsar, but the engine was a 220cc oil cooled one.
2012:
 Shows like Stunt mania and Pulsar fest emerged and gave a platform to budding stunt riders, but amongst all this Bajaj realised that they have an evolution of Pulsar series to plan ahead. What better way to make a fast bike better? Combine it with an even faster bike. Bajaj collaborated with KTM to make the ultimate new age Pulsar, the 200NS.
Shows like Stunt mania and Pulsar fest emerged and gave a platform to budding stunt riders, but amongst all this Bajaj realised that they have an evolution of Pulsar series to plan ahead. What better way to make a fast bike better? Combine it with an even faster bike. Bajaj collaborated with KTM to make the ultimate new age Pulsar, the 200NS. Pulsar 200 NS was built from the ground up using KTM’s technology, the perimeter frame, the 4-valve engine, the liquid cooling, all were borrowed from KTM and returned for a Pulsar. The bike produced 23 BHP of power and 18 NM of torque, it had a monoshock suspension instead of the dual-shock setup and a naked styling. It became famous for the stunt riding due to its amazing mass centralization and acceleration but ultimately it lost the competition to its cousin the Pulsar 220, which kept selling despite using an older technology.
2015:
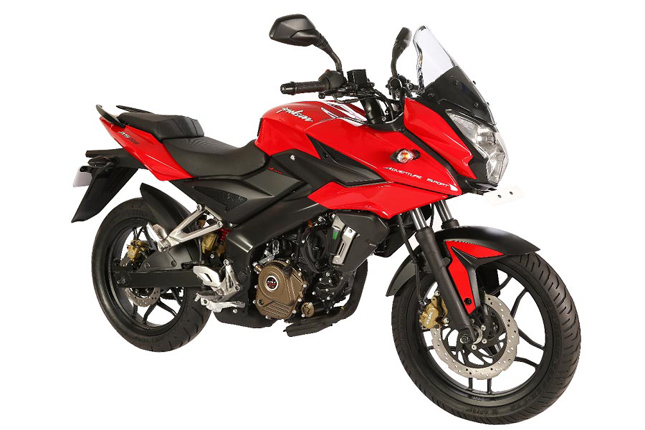 Bajaj was relentlessly working on something different this year, they were planning on making a successor to the Pulsar 220F. The bike which they introduced as it’s replacement was AS200, where AS stood for Adventure Sports. It had the same 199cc engine found in NS200 and even used the same perimeter frame. AS 200 was basically an NS200 with a new front section. It had a windscreen and a redesigned fairing which made it look like a modern Pulsar 220F, but despite having better technology and it was unable to defeat the sales of the original fastest Indian.
Bajaj was relentlessly working on something different this year, they were planning on making a successor to the Pulsar 220F. The bike which they introduced as it’s replacement was AS200, where AS stood for Adventure Sports. It had the same 199cc engine found in NS200 and even used the same perimeter frame. AS 200 was basically an NS200 with a new front section. It had a windscreen and a redesigned fairing which made it look like a modern Pulsar 220F, but despite having better technology and it was unable to defeat the sales of the original fastest Indian.
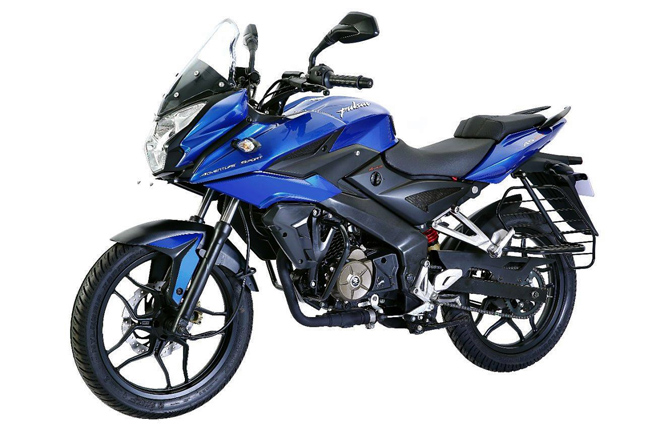 Another Adventure sports model was released this year which was known as AS 150. It had the same chassis and design as it’s elder brother the AS200, the only difference was in its equipment. It has an air cooled 150 cc engine with a rear drum brake, a skinnier tyre and swing arm. Though the bikes were great on-road, they were not suitable for dirt and mud as they lacked long travel suspensions and off-road tyres. These were discontinued in the late 2016 and in their place the new NS 200 was re-released.
Another Adventure sports model was released this year which was known as AS 150. It had the same chassis and design as it’s elder brother the AS200, the only difference was in its equipment. It has an air cooled 150 cc engine with a rear drum brake, a skinnier tyre and swing arm. Though the bikes were great on-road, they were not suitable for dirt and mud as they lacked long travel suspensions and off-road tyres. These were discontinued in the late 2016 and in their place the new NS 200 was re-released.
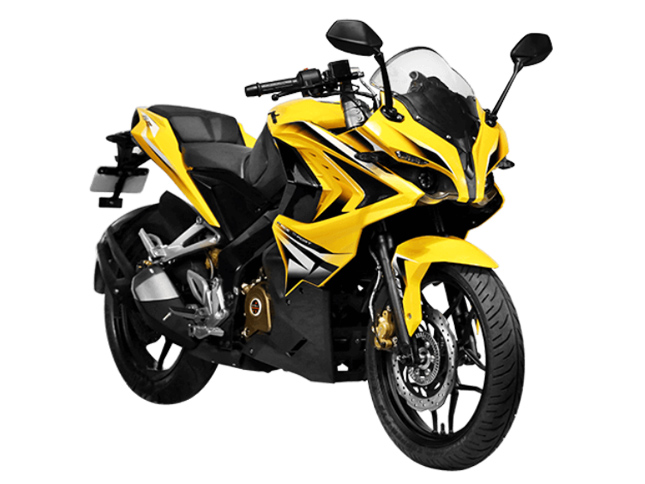 Pulsar 220F was starting to show its age, despite what it’s sales figure were, it was on the verge of becoming an outdated model. Bajaj knew that and was prepared to launch its successor, the Pulsar 200RS, where RS stood for 'Race sports'. This bike became the most controversial topic when it was launched due to its excessive styling. It had stickers all over the place, for some it was a good thing but for others, it was a deal breaker. On the engine side, the bike had a 199cc liquid cooled fuel injected 4 valve motor, which was very smooth and efficient. The 200RS became the new fastest Indian, with a top speed of 150 km/h.
Pulsar 220F was starting to show its age, despite what it’s sales figure were, it was on the verge of becoming an outdated model. Bajaj knew that and was prepared to launch its successor, the Pulsar 200RS, where RS stood for 'Race sports'. This bike became the most controversial topic when it was launched due to its excessive styling. It had stickers all over the place, for some it was a good thing but for others, it was a deal breaker. On the engine side, the bike had a 199cc liquid cooled fuel injected 4 valve motor, which was very smooth and efficient. The 200RS became the new fastest Indian, with a top speed of 150 km/h.
2018:
Pulsar 150 is going to get an upgrade in the form of a new rear disc brake, wide tyres and split seats, also reports are coming in of a new Pulsar in development and people are saying that it's going to be a 250 cc motorcycle. Although it doesn’t seem logical to use a 250 cc motor by boring a 200 cc one when you already have a 375 cc engine triple spark engine available. Anyways, we can expect the announcement of a new Pulsar this year.
For everything related to motorcycles, stay tuned to BikesMedia.
By: Yetnesh Dubey