We all are well aware that the world has moved on from the old school 2 strokes to modern 4 stroke machines. The reasons behind it are vastly due to fuel efficiency and cleaner emissions at the cost of outright power. The power factor is the most important advantage of two stroke engines, as there is one power stroke for each cycle whereas the 4 stroke counterpart produces one power stroke in each cycle. The cycle followed by 2 and 4 stroke engines are entirely different and that makes the reason behind this write up. What follows is a detailed differentiation between the two engines.
The Engine Cycles:
Before coming to the cycles of 2 and 4 stroke engines it is important to know about the working of the actual engines. Below are the two working models of both engines shown in the form of animation.
A four stroke petrol engine-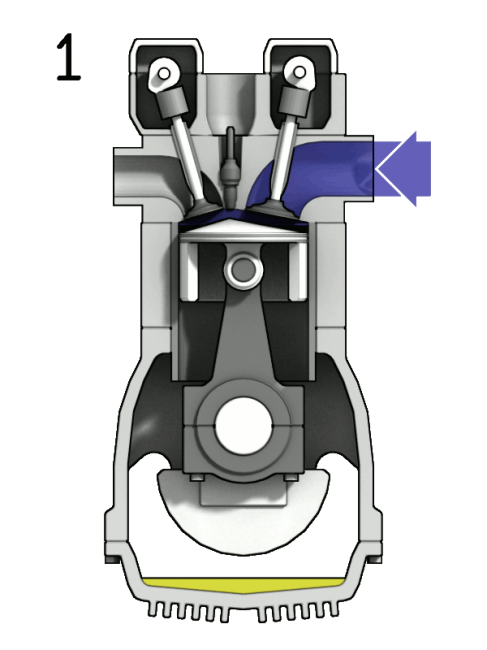 A four stroke engine is based on the Otto cycle. According to the Otto cycle, the four strokes which make one cycle is as follows.
A four stroke engine is based on the Otto cycle. According to the Otto cycle, the four strokes which make one cycle is as follows.
A 2 stroke petrol engine-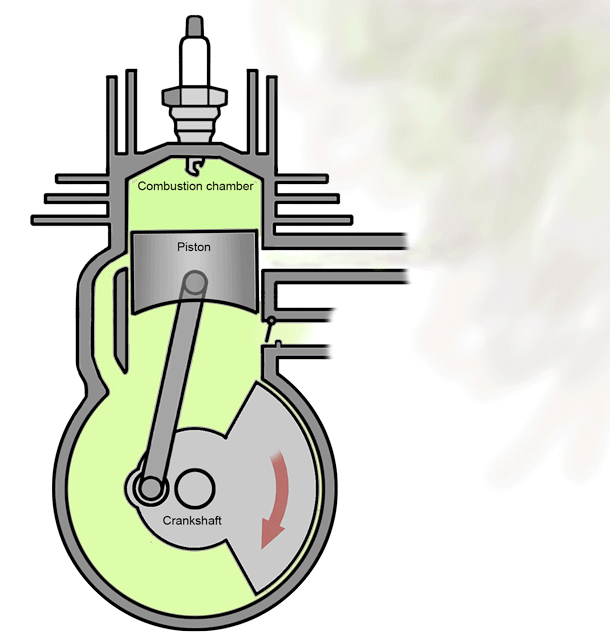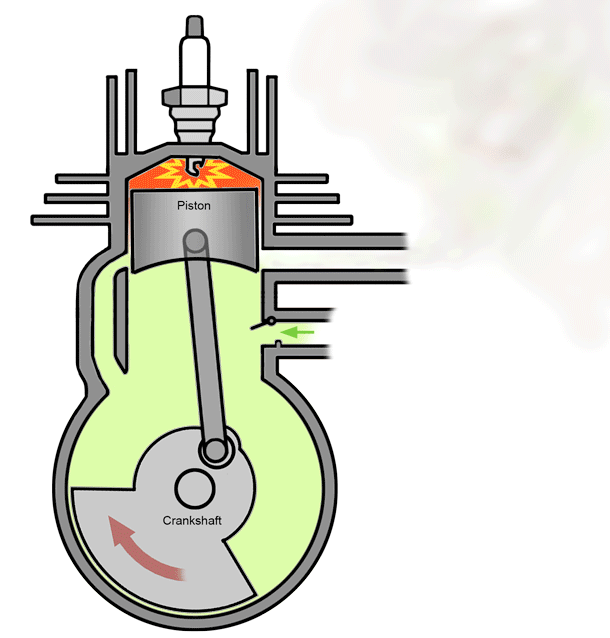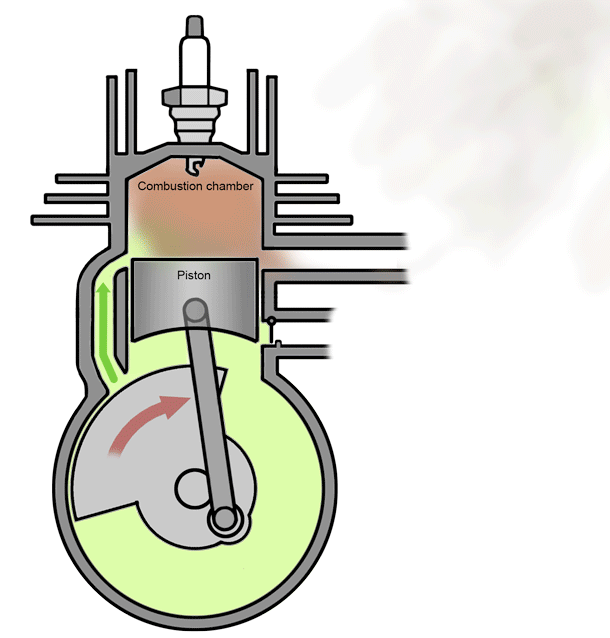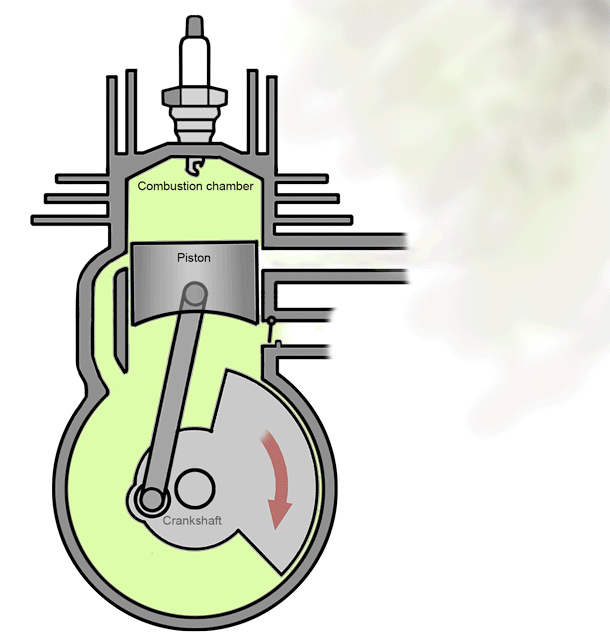 As the name suggests, these engines perform intake, compression, power and exhaust strokes in just two stroke of the piston, i.e; in one full rotation of the crankshaft.
As the name suggests, these engines perform intake, compression, power and exhaust strokes in just two stroke of the piston, i.e; in one full rotation of the crankshaft.
* Stroke 1 - End of combustion and beginning of compression happens together.
* Stroke 2 - Intake and exhaust occurs simultaneously.
This cycle is achieved by using three ports on the cylinder instead of having valves on the engine head. The piston is also uniquely designed in such a way that it helps the internal process. The inlet port gets the fuel mixture from the carburetor while the exhaust port releases the combusted exhaust gases. The third port is unique and is placed on the same level as the exhaust port at the bottom dead center (the maximum possible downward position the piston could reach).
RELATED ARTICLE: Why 2-Stroke Engines Are More Fun Than 4-Stroke Engines?
During the first stroke, the end of combustion takes place followed by the beginning of compression. On the next stroke, intake and exhaust occur simultaneously. Instead of having actual valves, the piston itself acts like a valve by sliding over the appropriate ports over each stroke. The transfer ports move the fresh fuel mixture to the combustion chamber and also helps in the process of scavenging. The 2 stroke racing engines needs to have a unique exhaust design in order to achieve the maximum scavenging possible, where the pipe has an expansion chamber before exhausting the gases. Looking at the picture below would make you clear regarding the internal ports.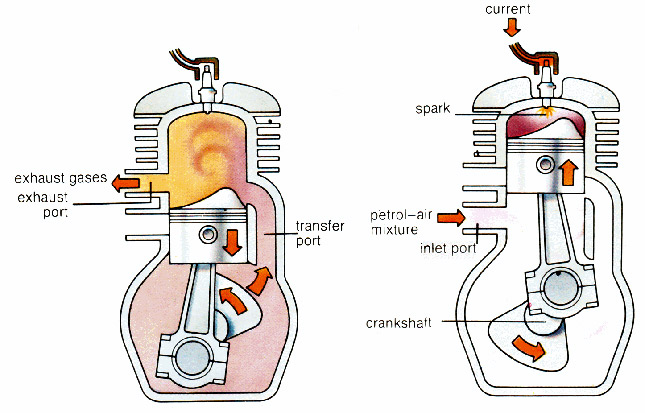 Environmental Pollution:
Environmental Pollution:
RELATED ARTICLE: Why 2-Stroke Engines Are Louder Than 4-Stroke Engines?
The first and foremost problem with two stroke engines is that it produces a large amount of carbon emissions through the exhaust. This is because of the mixing of fresh air fuel mixture in the exhaust gases. And that's the reason why two stroke machines produce a white fume of smoke. This partial amount of fuel getting mixed with the exhaust gases is ungovernable is most cases, which is the reason why 2 strokes are inefficient. That's why the world has moved on to much environment friendly 4 stroke engines, at a cost of having monstrous powerful engines.
By: Aravind Rb
The Engine Cycles:
Before coming to the cycles of 2 and 4 stroke engines it is important to know about the working of the actual engines. Below are the two working models of both engines shown in the form of animation.
A four stroke petrol engine-
 A four stroke engine is based on the Otto cycle. According to the Otto cycle, the four strokes which make one cycle is as follows.
A four stroke engine is based on the Otto cycle. According to the Otto cycle, the four strokes which make one cycle is as follows. * Stroke 1 - Intake (Piston moves from up to down).
* Stroke 2 - Compression (Piston moves down to up).
* Stroke 3 - Power (Spark plug works in this stroke. Piston moves from up to down).
* Stroke 4 - Exhaust (Piston moves down to up).
The valves open and close accordingly to the position of the piston. The intake valve/valves open during the stroke 1 and exhaust valve/valves open during stroke 4. The valves remain closed during the compression and power strokes. The valves are operated by using a timing chain and rocker arms. * Stroke 2 - Compression (Piston moves down to up).
* Stroke 3 - Power (Spark plug works in this stroke. Piston moves from up to down).
* Stroke 4 - Exhaust (Piston moves down to up).
A 2 stroke petrol engine-
 As the name suggests, these engines perform intake, compression, power and exhaust strokes in just two stroke of the piston, i.e; in one full rotation of the crankshaft.
As the name suggests, these engines perform intake, compression, power and exhaust strokes in just two stroke of the piston, i.e; in one full rotation of the crankshaft.* Stroke 1 - End of combustion and beginning of compression happens together.
* Stroke 2 - Intake and exhaust occurs simultaneously.
This cycle is achieved by using three ports on the cylinder instead of having valves on the engine head. The piston is also uniquely designed in such a way that it helps the internal process. The inlet port gets the fuel mixture from the carburetor while the exhaust port releases the combusted exhaust gases. The third port is unique and is placed on the same level as the exhaust port at the bottom dead center (the maximum possible downward position the piston could reach).

*** A two stroke Honda NSR500 used by Mick Doohan in Premier class racing.
RELATED ARTICLE: Why 2-Stroke Engines Are More Fun Than 4-Stroke Engines?
During the first stroke, the end of combustion takes place followed by the beginning of compression. On the next stroke, intake and exhaust occur simultaneously. Instead of having actual valves, the piston itself acts like a valve by sliding over the appropriate ports over each stroke. The transfer ports move the fresh fuel mixture to the combustion chamber and also helps in the process of scavenging. The 2 stroke racing engines needs to have a unique exhaust design in order to achieve the maximum scavenging possible, where the pipe has an expansion chamber before exhausting the gases. Looking at the picture below would make you clear regarding the internal ports.
 Environmental Pollution:
Environmental Pollution:RELATED ARTICLE: Why 2-Stroke Engines Are Louder Than 4-Stroke Engines?
The first and foremost problem with two stroke engines is that it produces a large amount of carbon emissions through the exhaust. This is because of the mixing of fresh air fuel mixture in the exhaust gases. And that's the reason why two stroke machines produce a white fume of smoke. This partial amount of fuel getting mixed with the exhaust gases is ungovernable is most cases, which is the reason why 2 strokes are inefficient. That's why the world has moved on to much environment friendly 4 stroke engines, at a cost of having monstrous powerful engines.
By: Aravind Rb











