A multi cylinder engine (say inline four configuration) has 4 pistons connected to corresponding crankshafts to convert the horizontal motion of the piston into a rotational motion. Ever since the early days, the crankshaft was designed to rotate in a direction similar to the direction of the rotating wheels. Back in those days the crankshaft, connecting rods and the piston balancing counterweights were so heavy that the conventional rotation of the crankshaft caused a kind of a gyroscopic force which can significantly affect a motorcycles handling characteristics and front end feel.
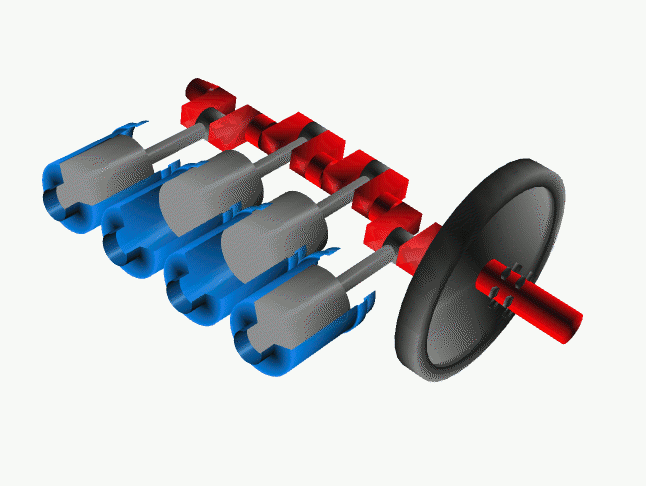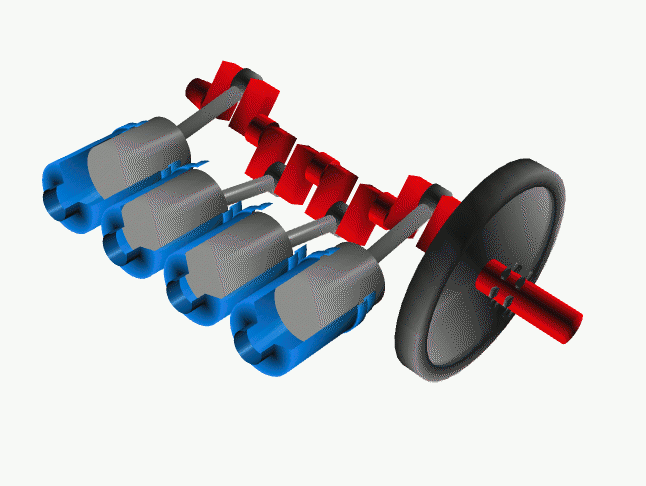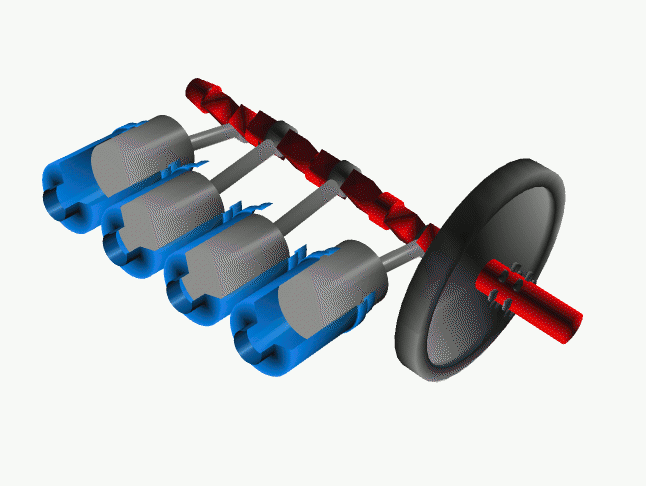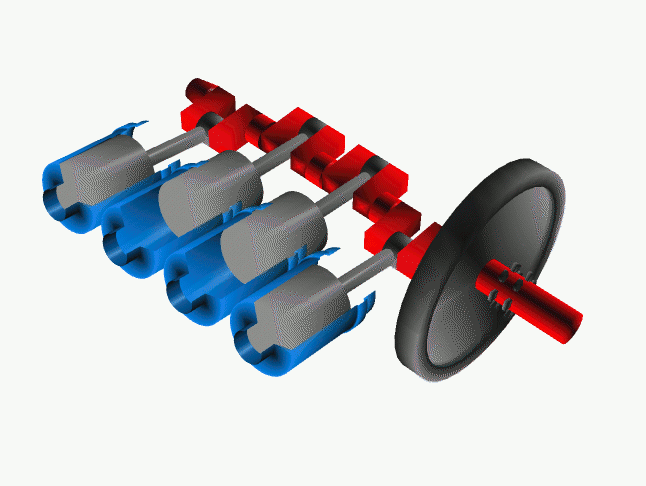
The Solution:
Though changing times resulted in better manufacturing technology and knowledge on strength of materials, the engineers were not convinced with that little bit of gyroscopic effect. So there came an idea to rotate the crankshaft in the opposite direction of the rotating wheels. By this change, the power wheelies under acceleration came down considerably as the gyroscopic force due to the heavy crankshaft now doesn't act upwards. But crankshaft rotating in the opposite direction means that, there needs to be an extra gear to convert the counter rotation. Only then the motorcycle would move in the desired forward direction.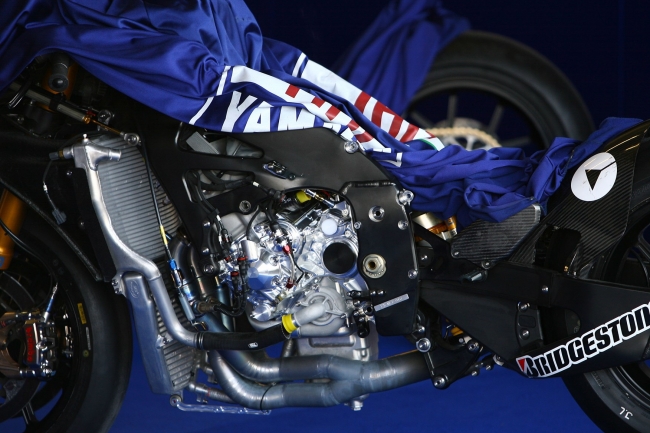 Counter Rotating Crank In MotoGP:
Counter Rotating Crank In MotoGP:
At present, the entire manufacturers competing in the Premier class of racing run their engines backwards with the use of counter rotating crankshafts. Yamaha and Suzuki were the ones to use this technology regularly since a very long period of time, though Honda and Ducati have joined a year ago. Honda Racing Corporation (HRC) were the pioneers in the Grand Prix racing in the 1980's, as they were the first to introduce a counter rotating crankshaft on their 1987 NSR 500, and then won eight of the last thirteen 500cc Championships. With present technology, the engine components are super light and the gyroscopic effect doesn't seem to be considerable. Yet, the engineers prove theoretically that rotating the engine in the opposite direction gives better stability to the bikes when going around the corners. But this comes at a price of putting an additional gear in the engine, which significantly reduces by engine horsepower by 7 to 8 bhp. This is one significant reason why the Hondas are not able to overtake the Yamahas on straights since 2016, in the way they did back in 2015. So everything has a catch in racing, making the pros and cons cancel out each other.
With present technology, the engine components are super light and the gyroscopic effect doesn't seem to be considerable. Yet, the engineers prove theoretically that rotating the engine in the opposite direction gives better stability to the bikes when going around the corners. But this comes at a price of putting an additional gear in the engine, which significantly reduces by engine horsepower by 7 to 8 bhp. This is one significant reason why the Hondas are not able to overtake the Yamahas on straights since 2016, in the way they did back in 2015. So everything has a catch in racing, making the pros and cons cancel out each other.
By: Aravind Rb

*** A conventional forward rotating crank setup
The Solution:
Though changing times resulted in better manufacturing technology and knowledge on strength of materials, the engineers were not convinced with that little bit of gyroscopic effect. So there came an idea to rotate the crankshaft in the opposite direction of the rotating wheels. By this change, the power wheelies under acceleration came down considerably as the gyroscopic force due to the heavy crankshaft now doesn't act upwards. But crankshaft rotating in the opposite direction means that, there needs to be an extra gear to convert the counter rotation. Only then the motorcycle would move in the desired forward direction.
 Counter Rotating Crank In MotoGP:
Counter Rotating Crank In MotoGP:At present, the entire manufacturers competing in the Premier class of racing run their engines backwards with the use of counter rotating crankshafts. Yamaha and Suzuki were the ones to use this technology regularly since a very long period of time, though Honda and Ducati have joined a year ago. Honda Racing Corporation (HRC) were the pioneers in the Grand Prix racing in the 1980's, as they were the first to introduce a counter rotating crankshaft on their 1987 NSR 500, and then won eight of the last thirteen 500cc Championships.
 With present technology, the engine components are super light and the gyroscopic effect doesn't seem to be considerable. Yet, the engineers prove theoretically that rotating the engine in the opposite direction gives better stability to the bikes when going around the corners. But this comes at a price of putting an additional gear in the engine, which significantly reduces by engine horsepower by 7 to 8 bhp. This is one significant reason why the Hondas are not able to overtake the Yamahas on straights since 2016, in the way they did back in 2015. So everything has a catch in racing, making the pros and cons cancel out each other.
With present technology, the engine components are super light and the gyroscopic effect doesn't seem to be considerable. Yet, the engineers prove theoretically that rotating the engine in the opposite direction gives better stability to the bikes when going around the corners. But this comes at a price of putting an additional gear in the engine, which significantly reduces by engine horsepower by 7 to 8 bhp. This is one significant reason why the Hondas are not able to overtake the Yamahas on straights since 2016, in the way they did back in 2015. So everything has a catch in racing, making the pros and cons cancel out each other.By: Aravind Rb











